| Introduction
Electro-optic Pockels cells are used in applications that require fast switching of the polarization direction of a beam of light. These uses include Q-switching of laser cavities, coupling light into and out from regenerative amplifiers, and, when used in conjunction with a pair of polarizers, light intensity modulation. Pockels cells are characterized by fast response, since the Pockels Effect is largely an electronic effect that produces a linear change in refractive index when an electric field is applied, and are much faster in response than devices based on acoustic changes in a material, for example. When
an electric field (E) is applied to an electro-optic (E-O)
crystal, the refractive index of E-O crystal will change linearly to electric field. The
phenomenon is called linear electro-optic effect. For KD*P
crystal, for example, the change of the refractive index
(Dn) is
Dn = 0.5n3or63E
if both the directions of light propagation and electric
field are along the z-axis, where no is refractive
index without electric field and r63 is electro-optic
coefficient of KD*P. change linearly to electric field. The
phenomenon is called linear electro-optic effect. For KD*P
crystal, for example, the change of the refractive index
(Dn) is
Dn = 0.5n3or63E
if both the directions of light propagation and electric
field are along the z-axis, where no is refractive
index without electric field and r63 is electro-optic
coefficient of KD*P.
If a
linearly polarized light passes through an E-O crystal,
the phase retardation (G) will
be induced by Dn to
G = 2pDnL, where
L is crystal length, for KD*P, again as an example, G = pLn3or63E/l. It
is clear that the phase of light will change together with
electric field (E). This is called electro-optic phase modulation.
If two crossed polarizers are placed at input and output
ends of E-O crystal separately, the output intensity of
light will be I = I0sin2(G/2),
where I0 is input intensity. That means the intensity
or amplitude of light can also be modulated by electric
field. This is called amplitude modulation.
 |
 |
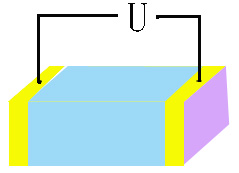
| longitudinal
E-O modulation |
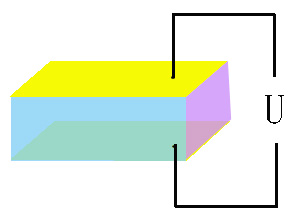
transverse
E-O modulation |
There
are two kinds of E-O modulations. One
is longitudinal E-O modulation if the directions of electric
field and light propagation are the same. The KDP isomorphic
crystals are normally used in this scheme. If the directions
of electric field and light propagation are perpendicular,
it is called transverse E-O modulation. The LiNbO3, MgO:LiNbO3, ZnO:LiNbO3, BBO
and KTP crystals are usually employed in this scheme.
The half-wave
voltage (Vp) is
defined as the voltage at G = p, for
example, Vp=l/(2no3r63) for KD*P
and Vp=ld/(2no3r22L)
for LiNbO3, where
l is light
wavelength and d is the distance between the electrodes.
Electro-Optic
Crystals and Acousto-Optic Crystals: LiTaO3;
BSO; BGO; TeO2; PbMoO4, etc. |



